Tig из mig

MIG vs TIG Welding: Which One is the Right Choice?
Welding is the process of fusing separate pieces of metal into a single unit. It uses heat to create a small pool of molten metal, which is moved along the joint region to weld the pieces together. Many heating methods are used, but metal fabricators rely primarily on the electric arc.











MIG vs TIG Welding
Which is to say, it is enormous. Inert gas is used to protect or shield the weld pool. In many cases, particularly when the welds have to be small and look good, TIG welding is the way to go. He is welding stainless tube cut on our tube laser to a stainless steel sheet cut on one of our flat lasers and formed.








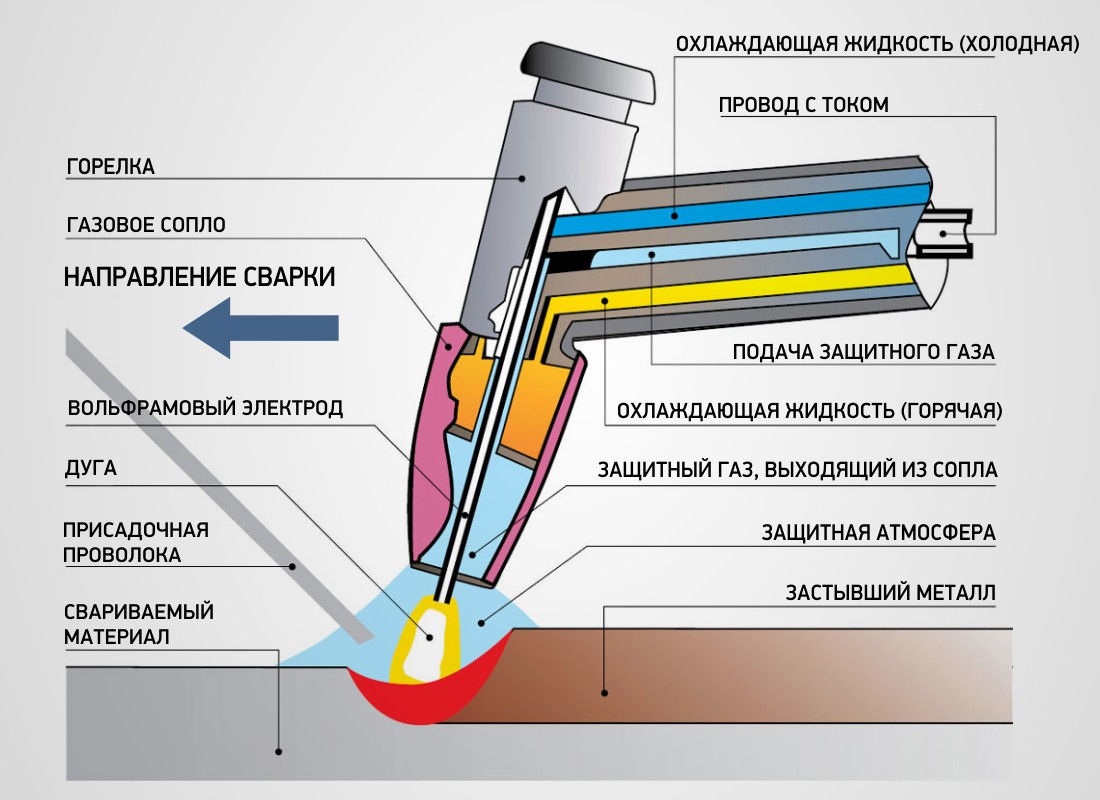
MIG and TIG welding are common types of welding with a number of similarities, as they both use an electric arc and a shielding gas. However, there are a number of differences between the two processes, including with the welding electrodes used to create the arc. MIG uses a solid wire that is machine-fed to the weld area while TIG uses a non-consumable electrode and a hand-held filler rod to form the weld.







